// Documenti disponibili n: 46.227
// Documenti scaricati n: 35.938.671
This is currently under committee review, with an expectation that it will be available quite soon as ISO/TR 24119.
This TR has not been published but it will deal with.
The Technical Report illustrates and explains principles of fault masking in applications where multiple interlocking devices with potential free contacts are connected in series to one logic unit which does the diagnostics.
It provides also a guide how to estimate the probability of fault masking and the maximum DC for the involved position switches.
In simple terms, if we have more than one frequently opened guard (once per hour) the level of Diagnostic Coverage falls to zero, which in EN ISO 13849-1 results in a maximum PLc.
It remains to be seen exactly what ISO/PDTR 24119 has to say about the maximum PL achievable when several infrequently operated guards are connected, but it is very likely to be PLd where careful analysis is possible (for example, the number of guards, the type of switches, type of wiring, distance between guards, and accessibility of guards), otherwise it is more likely to be PLc.
It is definitely not possible to achieve PL e with more than one guard switch connected in series, at least not when using volt-free based interlock switch technology.
Early signs are that the technical report ISO/PDTR 24119 will provide two methods for evaluating the extent to which diagnostic coverage is impacted by masking:
1. Simplified method for the determination of the maximum achievable DC
Table 1 provides a simplified approach for the determination of the maximum achievable DC taking into account the probability of masking.
If the maximum achievable DC resulting from the application of this table does not meet the required level, the more detailed approach given in 2 may be more suitable - but this is not ideal.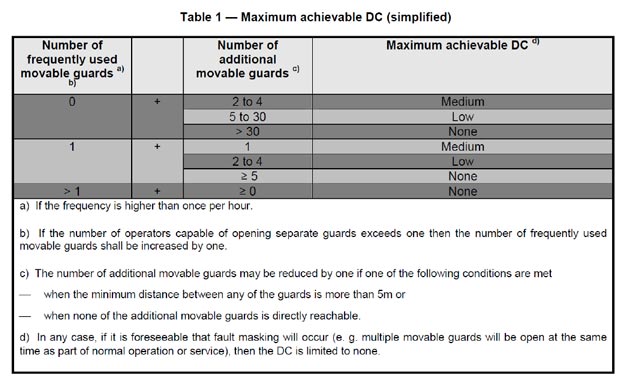
2. Regular method for the determination of the maximum achievable DC
2.1 Estimation of the fault masking probability
The probability of fault masking is dependent on several parameters that should be considered, including:
The maximum achievable DC depends on the fault masking probability level (FM) and the type of cabling used in combination with the switch arrangement and the diagnostic capabilities of the overall system to detect faults.
Tables 3 to 5 show the maximum reachable DC depending on those parameters.
In any case, if it is foreseeable that fault masking will occur (eg multiple movable guards will be open at the same time as part of normal operation or service), then the DC is limited to none.
It is beyond the scope of this article to go into the details of tables 3 and 5 referred to above, and it is recommended that, instead, the 'simplified method outlined in 2 above is used.
...
in allegato Preview

ID 22550 | 13.09.2024
Decisione di esecuzione (UE) 2024/2406 della Commissione, del 12 settembr...

ID 24564 | 10.09.2025 / In allegato
Decisione di esecuzione (UE) 2025/1785 della Commissione, del 9 settemb...

ID 23496 | 20.02.2025 / In allegato Preview
CEI EN 60598-2-22:2023
Apparecchi di illuminazione
Parte 2-22: Prescrizioni particolari - Apparecchi di emergen...
Testata editoriale iscritta al n. 22/2024 del registro periodici della cancelleria del Tribunale di Perugia in data 19.11.2024