This document specifies symbols used to express information supplied for a medical device. This document is applicable to symbols used in a broad spectrum of medical devices, that are available globally and need to meet different regulatory requirements.
These symbols can be used on the medical device itself, on its packaging or in the accompanying information. The requirements of this document are not intended to apply to symbols specified in other standards.
This fourth edition cancels and replaces the third edition (ISO 15223-1:2016), which has been technically revised.
The main changes compared to the previous edition are as follows:
- addition of 20 symbols that were validated as per ISO 15223-2;
- addition of 5 symbols previously published in ISO 7000, ISO 7001 and IEC 60417;
- deletion of the defined term “labelling”;
- inclusion of defined terms from ISO 20417, ISO 13485 and ISO 14971;
- expansion of the examples given in Annex A;
- information about European regulations has been moved to informative notes throughout
Introduction
Medical device manufacturers and others in the supply chain must provide specific information on the medical device itself, as part of the packaging, or in the accompanying information. For simplicity and to avoid translation of text, this information can be provided as symbols that have a specific meaning. This document does not specify the information that needs to be provided, but does specify internationally recognized symbols for the provision of this specific information.
The symbols included in this document have been published in ISO 7000, ISO 7001, IEC 60417 or have been subjected to a formal symbol validation process.
This document is intended to be used by manufacturers of medical devices who market products in countries where there are specific language requirements. These symbols allow for a consistent portrayal of information. It can also be used by consumers or end users of medical devices who draw their supplies from a number of sources and can have varied language capabilities.
In this document, the conjunctive “or” is used as an “inclusive or”; so a statement is true if any combination of the conditions is true.
Terms defined in Clause 3 are shown in italic type throughout the document.
In this document, the following verbal forms are used:
- “shall” indicates a requirement;
- “should” indicates a recommendation;
- “may” indicates a permission;
- “can” indicates a possibility or a capability;
- “must” indicates an external constraint that is not a requirement of the document.
Information marked as “NOTE” is intended to assist the understanding or use of the document. “Notes to entry” used in Clause 3 provide additional information that supplements the terminological data and can contain provisions relating to the use of a term.
Symbols added during the revision of this document were placed at the end of the pertinent section of Table 1 to preserve the numbering of existing symbols and facilitate easy referencing of existing symbols in other documents.
NOTE Numbers given in square brackets throughout the document refer to the Bibliography.
1 Scope
This document specifies symbols used to express information supplied for a medical device. This document is applicable to symbols used in a broad spectrum of medical devices, that are available globally and need to meet different regulatory requirements.
These symbols can be used on the medical device itself, on its packaging or in the accompanying information. The requirements of this document are not intended to apply to symbols specified in other standards.
2 Normative references
The following documents are referred to in the text in such a way that some or all of their content constitutes requirements of this document. For dated references, only the edition cited applies. For undated references, the latest edition of the referenced document (including any amendments) applies.
ISO 3166-1, Codes for the representation of names of countries and their subdivisions - Part 1: Country code
ISO 8601-1, Date and time - Representations for information interchange - Part 1: Basic rules
ISO 8601-2, Date and time - Representations for information interchange - Part 2: Extensions
ISO 15223-2, Medical devices - Symbols to be used with medical device labels, labelling, and information to be supplied - Part 2: Symbol development, selection and validation
3 Terms and definitions
For the purposes of this document, the following terms and definitions apply.
ISO and IEC maintain terminological databases for use in standardization at the following addresses:
- ISO Online browsing platform: available at https://www.iso.org/obp
- IEC Electropedia: available at http://www.electropedia.org/
3.1
accompanying information
information accompanying or marked on a medical device or accessory for the user or those accountable for the installation, use, processing, maintenance, decommissioning and disposal of the medical device or accessory, particularly regarding safe use
Note 1 to entry: The accompanying information shall be regarded as part of the medical device or accessory.
Note 2 to entry: The accompanying information can consist of the label, marking, instructions for use, technical description, installation manual, quick reference guide, etc.
Note 3 to entry: Accompanying information is not necessarily a written or printed document but could involve auditory, visual, or tactile materials and multiple media types (e.g. CD/DVD-ROM, USB stick, website).
Note 4 to entry: See Figure 1.
Note 5 to entry: The label can include the information on the packaging of the medical device.
Note 6 to entry: e-documentation can include any or all types of information supplied by the manufacturer partially or entirely.
Note 7 to entry: Marketing information is also known as promotional material.
Note 8 to entry: There is guidance or rationale related to accompanying information in ISO 20417:2021,[15] Annex A.
Figure 1 - Relationship of terms used to describe information supplied by the manufacturer
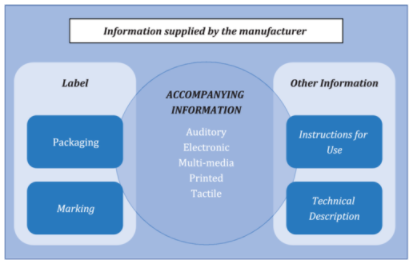
[SOURCE: ISO 20417:2021,[15] 3.2, modified — The following text has been removed from the graphic: “Scope of ISO 20417”, defined term reference numbers and a side box containing information outside the scope of ISO 20417. Note 8 to entry has been added.]
3.2
catalogue number
commercial product name
commercial product code
value given by the manufacturer to identify a specific medical device or accessory as it relates to its form/fit, function and process (i.e. manufacturing processes requiring differentiation for the end user)
Note 1 to entry: A catalogue number shall consist of letters or numbers or a combination of these.
Note 2 to entry: For the purposes of this document, commercial product code should not be confused with the US FDA, “product code” or procode classification.
Note 3 to entry: Synonyms for catalogue number are “reference number” or “reorder number”.
Note 4 to entry: See ISO 20417:2021, Figure 2.
[SOURCE: ISO 20417:2021,[15] 3.3, modified — The cross-reference in Note 4 to entry has been revised to be external to this document.]
3.3
description
normative text which defines the purpose, the application and the use of the symbol (3.19)
[SOURCE: IEC 80416-1:2008,[19] 3.2, modified - “and optional product area” has been removed.]
3.4
distributor
natural or legal person, different from the manufacturer or importer, in the supply chain who, on their own behalf, furthers the availability of a medical device or accessory to the user
Note 1 to entry: More than one distributor may be involved in the supply chain.
Note 2 to entry: For the purposes of this document, persons in the supply chain involved in activities such as storage and transport on behalf of the manufacturer, importer or distributor, are not distributors.
Note 3 to entry: Distribution activities alone do not include repackaging or otherwise changing the container, wrapper, or accompanying information of the medical device or medical device package other than providing the identification of the distributor.
[SOURCE: ISO 20417:2021,[15] 3.5]
3.5
importer
natural or legal person who imports a medical device or accessory into a locale that was manufactured in another locale for the purposes of marketing
[SOURCE: ISO 20417:2021,[15] 3.8]
3.6
information supplied by the manufacturer
information related to the identification and use of a medical device or accessory, in whatever form provided, intended to ensure the safe and effective use of the medical device or accessory
Note 1 to entry: For the purposes of this document, e-documentation is included in information supplied by the manufacturer.
Note 2 to entry: For the purposes of this document, shipping documents and promotional material are excluded from information supplied by the manufacturer. However, some authorities having jurisdiction (defined in ISO 16142-1:2016,[9] 3.1) can consider such supplemental information as information supplied by the manufacturer.
Note 3 to entry: The primary purpose of information supplied by the manufacturer is to identify the medical device and its manufacturer, and provide essential information about its safety, performance, and appropriate use to the user or other relevant persons.
Note 4 to entry: See Figure 1.
Note 5 to entry: There is guidance or rationale related to information supplied by the manufacturer in Annex A.
[SOURCE: ISO 20417:2021,[15] 3.10, modified - The cross-reference in Note 2 to entry has been added. Note 5 to entry has been added.]
3.7
instructions for use
IFU
package insert
portion of the accompanying information that is essential for the safe and effective use of a medical device or accessory directed to the user of the medical device
Note 1 to entry: For the purposes of this document, a user can be either a lay user or professional user with relevant specialized training.
Note 2 to entry: For the purposes of this document, instructions for the professional processing between uses of a medical device or accessory can be included in the instructions for use.
Note 3 to entry: The instructions for use, or portions thereof, can be located on the display of a medical device or accessory.
Note 4 to entry: Medical devices or accessories that can be used safely and effectively without instructions for use are exempted from having instructions for use by some authorities with jurisdiction.
Note 5 to entry: See Figure 1.
[SOURCE: ISO 20417:2021,[15] 3.11]
3.8
label
<medical device, accessory> written, printed or graphic information appearing on the item itself, on the packaging of each item, or on the packaging of multiple items
Note 1 to entry: For the purposes of this document, the term labelled is used to designate the corresponding act.
Note 2 to entry: Label includes the marking on the medical device or accessory.
Note 3 to entry: For the purposes of this document, information indicated on a graphical user interface (GUI) is considered as appearing on the item.
Note 4 to entry: See Figure 1.
[SOURCE: ISO 20417:2021,[15] 3.12]
3.9
lot number
batch code
batch number
lot code
production control containing a combination of letters or numbers associated with a single lot or batch
Note 1 to entry: The title of symbol 5.1.5 uses the synonym batch code.
[SOURCE: ISO 20417:2021,[15] 3.15, modified — Note 1 to entry has been added.]
3.10
manufacturer
natural or legal person with responsibility for the design or manufacture, or both, of a medical device with the intention of making the medical device available for use, under his or her name; whether or not such a medical device is designed or manufactured, or both, by that person themselves or on their behalf by another person(s)
Note 1 to entry: The natural or legal person has ultimate legal responsibility for ensuring compliance with all applicable regulatory requirements for the medical devices in the countries or jurisdictions where it is intended to be made available or sold, unless this responsibility is specifically imposed on another person by the Regulatory Authority (RA) within that jurisdiction.
Note 2 to entry: The manufacturer’s responsibilities are described in other GHTF guidance documents. These responsibilities include meeting both pre-market requirements and post-market requirements, such as adverse event reporting and notification of corrective actions.
Note 3 to entry: “Design or manufacture, or both”, may include specification development, production, fabrication, assembly, processing, packaging, repackaging, labelling, relabelling, sterilization, installation, or remanufacturing of a medical device; or putting a collection of devices, and possibly other products, together for a medical purpose.
Note 4 to entry: Any person who assembles or adapts a medical device that has already been supplied by another person for an individual patient, in accordance with the instructions for use, is not the manufacturer, provided the assembly or adaptation does not change the intended use of the medical device.
Note 5 to entry: Any person who changes the intended use of, or modifies, a medical device without acting on behalf of the original manufacturer and who makes it available for use under his own name, should be considered the manufacturer of the modified medical device.
Note 6 to entry: An authorized representative, distributor or importer who only adds its own address and contact details to the medical device or the packaging, without covering or changing the existing labelling, is not considered a manufacturer.
Note 7 to entry: To the extent that an accessory is subject to the regulatory requirements of a medical device, the person responsible for the design, manufacture, or both, of that accessory is considered to be a manufacturer.
[SOURCE: ISO 14971:2019,[8] 3.9]
3.11
marking
information, in text or graphical format, durably affixed, printed, etched (or equivalent) to a medical device or accessory
Note 1 to entry: For the purposes of this document, the term marked is used to designate the corresponding act.
Note 2 to entry: For the purposes of this document, marking is different from “direct marking” as commonly described in unique device identification (UDI) standards and regulations. A UDI “direct marking” is a type of marking.
Note 3 to entry: See Figure 1.
[SOURCE: ISO 20417:2021,[15] 3.16]
3.12
medical device
instrument, apparatus, implement, machine, appliance, implant, reagent for in vitro use, software, material or other similar or related article, intended by the manufacturer to be used, alone or in combination, for human beings, for one or more of the specific medical purpose(s) of:
- diagnosis, prevention, monitoring, treatment or alleviation of disease;
- diagnosis, monitoring, treatment, alleviation of or compensation for an injury;
- investigation, replacement, modification, or support of the anatomy or of a physiological process;
- supporting or sustaining life;
- control of conception;
- disinfection of medical devices;
- providing information by means of in vitro examination of specimens derived from the human body;
and does not achieve its primary intended action by pharmacological, immunological or metabolic means, in or on the human body, but which may be assisted in its intended function by such means
Note 1 to entry: Products which may be considered to be medical devices in some jurisdictions but not in others include:
- disinfection substances;
- aids for persons with disabilities;
- devices incorporating animal or human tissues, or both;
- devices for in vitro fertilization or assisted reproduction technologies.
[SOURCE: ISO 13485:2016,[7] 3.11]
3.13
model number
model
letters, numbers or a combination of these assigned by a manufacturer to distinguish by function or type, a particular medical device, accessory or medical device family from another
Note 1 to entry: See ISO 20417:2021, Figure 2.
[SOURCE: ISO 20417:2021,[15] 3.17, modified — The cross-reference in Note 1 to entry has been revised to be external to this document.]
3.14
risk
combination of the probability of occurrence of harm and the severity of that harm
[SOURCE: ISO 14971:2019,[8] 3.18]
3.15
serial number
production control containing a combination of letters or numbers, selected by the manufacturer, intended for quality control and identification purposes to uniquely distinguish an individual medicaldevice from other medical devices with the same catalogue number or model number
[SOURCE: ISO 20417:2021,[15] 3.22]
3.16
single patient multiple use
<medical device, accessory> intended by the manufacturer to be reused on an individual patient for multiple uses
Note 1 to entry: A single patient multiple use medical device or accessory may require processing between uses.
Note 2 to entry: For an implantable medical device, the duration of a single use is from implanting to explanting the medical device.
[SOURCE: ISO 20417:2021,[15] 3.25]
3.17
single use
do not re-use
use only once
<medical device, accessory> intended by the manufacturer to be used on an individual patient or specimen during a single procedure and then disposed of
Note 1 to entry: A single use medical device or accessory is not intended by its manufacturer to be further processed and used again.
[SOURCE: ISO 20417:2021,[15] 3.26]
3.18
sterile
free from viable microorganisms
[SOURCE: ISO 20417:2021,[15] 3.28]
3.19
symbol
graphical representation appearing on the label or associated documentation, or both, of a medical device that communicates characteristic information without the need for the supplier or receiver of the information to have knowledge of the language of a particular nation or people
Note 1 to entry: The symbol can be an abstract pictorial or a graphical representation, or one that uses familiar objects, including alphanumeric characters (with sufficient justification).
...
New Symbols for ISO 15223-1:2021
Firstly, these are the general new symbols:
Symbols if the device is a Medical Device (MD) or In-Vitro Diagnostic (IVD).
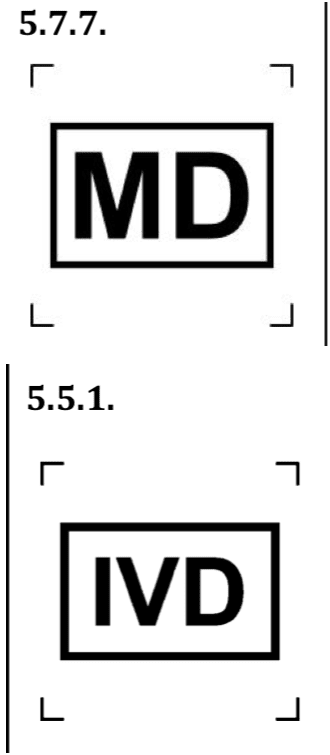
Moreover, for the IVD symbol, it is important to mention that the symbols is to identify in-vitro diagnostic devices and not medical devices to be used in vitro.
Symbols to identify the repackaging of a device.
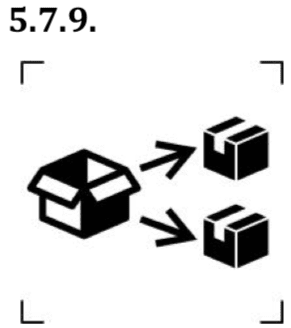
This symbol means that a modification of the original medical device packaging has been performed. The name and address of the responsible for repackaging activity shall be mentioned adjacent to the symbol. This symbols is used only when the repackaging is not performed by the manufacturer.
UDI symbol.

The UDI symbols is optional. When multiple data carrier are present on the label, the symbol may be used.
Name of the patient (for particular medical device).
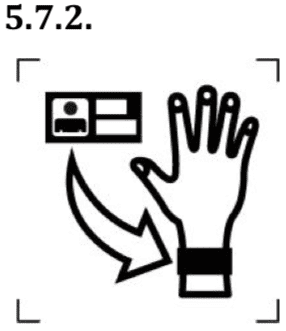
The symbol indicates the name of the patient
[...] Segue in allegato
Certifico Srl - EN | Rev. 1.0 2022
©Copia autorizzata Abbonati
Fonte: ISO
| Rev. |
Data |
Oggetto |
Autore |
| 1.0 |
10.11.2022 |
Pubblicata CEI UNI EN ISO 15223-1:2021 |
Certifico Srl |
| 0.0 |
12.07.2021 |
--- |
Certifico Srl |
Info e download
Collegati
Linee guida Regolamento Medical Devices (UE) 2017/745
MDR Regolamento dispositivi medici | Reg. (UE) 2017/745
Il Regolamento Dispositivi Medici (UE) 2017/745 - (MDR)
Faq Unique Device Identification (UDI) System